IV.A. ChimeraX Viewing Biological vs. Asymmetric Units
Walter Novak and Josh Beckham
Overview: The activity in this chapter demonstrates different ways to display structures (e.g., biological vs. asymmetric units).
Outcome: The user will explore different tools to load/display information related to biological/asymmetric units.
Time to complete: 10 minutes
Modeling Skill
- Displaying biological vs. asymmetric units
About the Model
PDB ID: 1HHO
Protein: Oxy-hemoglobin
Activity: gas transport in red blood cells
Description: tetramer, bound heme prosthetic group with bound oxygen, phosphate ligand
Background
The asymmetric unit of a crystal structure can represent either: (a) the complete biological unit (i.e., the biochemically active form of a biomolecule); (b) a portion of the biological unit; or (c) multiple copies of the biological unit. The “asymmetric unit” is equivalent to the biological unit (correct oligomeric functional state) in approximately 60% of structure records. The RCSB PDB has a detailed page explaining the asymmetric unit, with examples; see also the chapter in this book A Guide to PDB Structures and the RCSB PDB.
mmCIF Files
By default, ChimeraX opens Macromolecular Crystallographic Information File (mmCIF) files with the “open” command, which loads the asymmetric unit of the crystal structure. Sometimes this is the biological unit; however, sometimes this will miss a part of the biological unit—and sometimes it will contain more than one biological unit!
In the command line, type: open 1HHO
ChimeraX will note in the ”command log” if there are biological assemblies. To view the assembly, simply click on the blue number in the log window (shown below in Figure 1 with a yellow arrow).
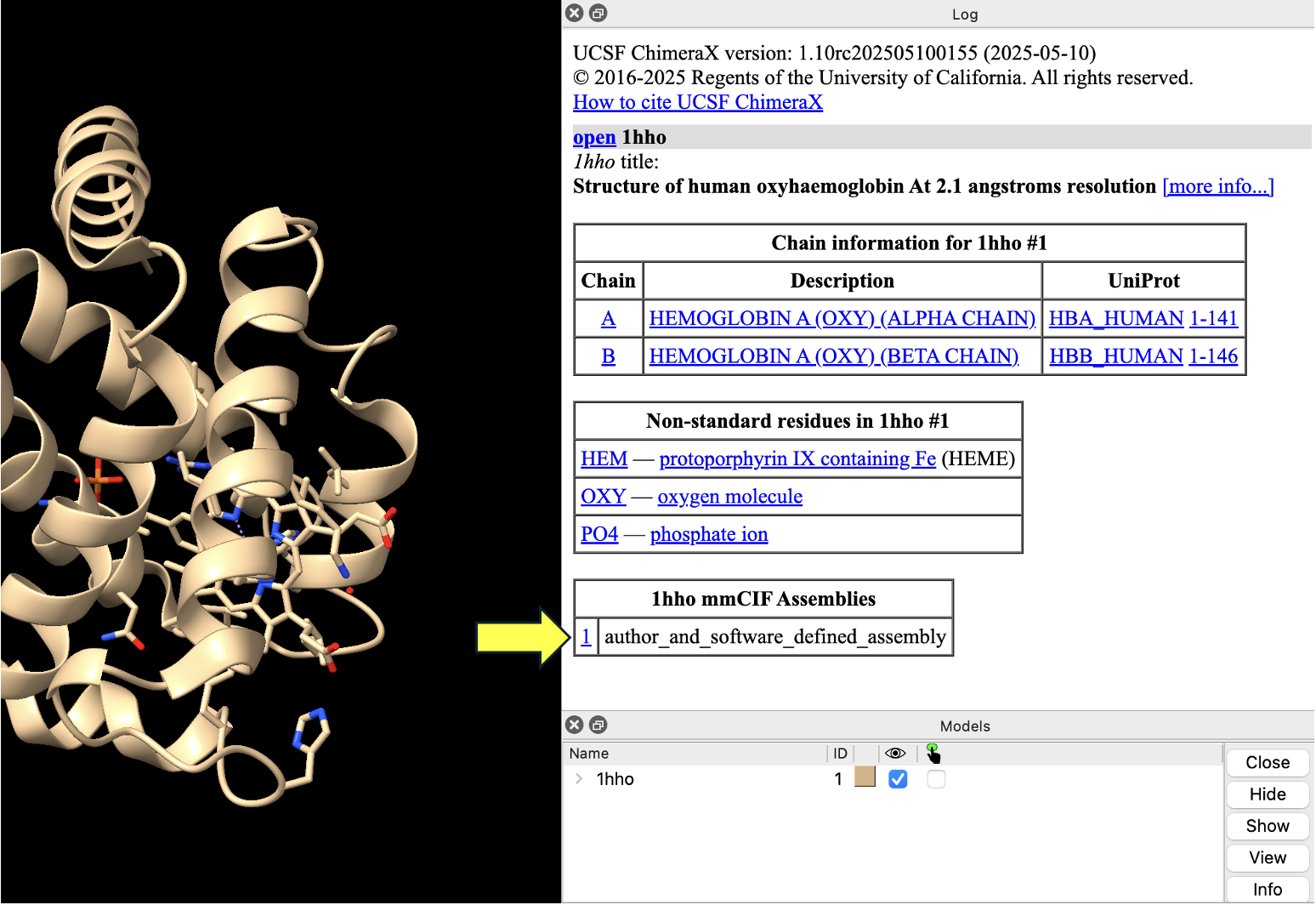
Note: If the log menu gets closed, you can open it again in the dropdown menu: Tools → Log.
After displaying the biological assembly, you should see multiple models in the ”Models” panel. Experiment with coloring your model by chain. (Select “Toolbar” → Model Display, then in the “Coloring” toolbar, click “Chain.”)
PDB Files
PDB files are the legacy format for the Protein Data Bank. You can open these with the “open” command as well:
open 1hho format pdb
ChimeraX will not automatically display whether there is a biological assembly if you force it to download a pdb file. However, you can still display the biological unit if it differs from the asymmetric unit using the command:
sym #1 biomt
The “sym #1” command generates a symmetry mate for model #1. The option “biomt” tells sym to use the biological transformation matrix.
Going Deeper
About the Model
PDB ID: 6Y2E
Protein: SARS CoV-2 main protease
Activity: Proteolytic enzyme
Description: Dimeric enzyme that activates viral proteins
Steps
- Load this file into ChimeraX using the “open” command.
open 6y2e
- Explore the different assemblies by clicking on them in the log.
What is shown in each assembly? Consider a scenario where you need to examine the biological unit. Consider a scenario when you don’t need the biological unit.
To see the unit cell:
- In the dropdown menu: Tools → Higher Order Structure → Unit Cell.
- In the “Unit Cell” toolbox that opens at the bottom right of the Model Panel, select “Outline” and then “Make Copies”.
NOTE: To re-center everything, type view in the command line.
- (Optional) Save and close the session.
Jump to the next ChimeraX tutorial: V.A. ChimeraX Mouse/Trackpad Selection.
